Knowledge Hub
Pharmacological vs
Exercise Stress Echocardiography
An echocardiogram can help build a comprehensive picture of the heart in action. This is frequently used in medical practices to help diagnose and monitor a varied range of heart conditions.
In this article, we discuss two subtypes of the stress echocardiogram: pharmacological and exercise stress tests. We explore the differences between the two, and which one is potentially better for patients.
What is Stress Echocardiography?
A stress echocardiogram monitors how the heart performs whilst under stress; this means how it copes with an increased heart rate. The optimal heart rate is based on the age of the individual being tested.
Echocardiograms are created through ultrasound, or sound waves, which capture live images of the heart whilst it is at rest, and then whilst it is working at an elevated pace. The two sets of images can then be compared.
Medical professionals can use this information to evaluate a range of heart conditions, including:
- The size of the heart
- Abnormal valves
- Problems with the aorta
- Blood clots
- Inflammation or fluid in the sac around the heart
- Ability of the heart to pump and relax
- Murmurs
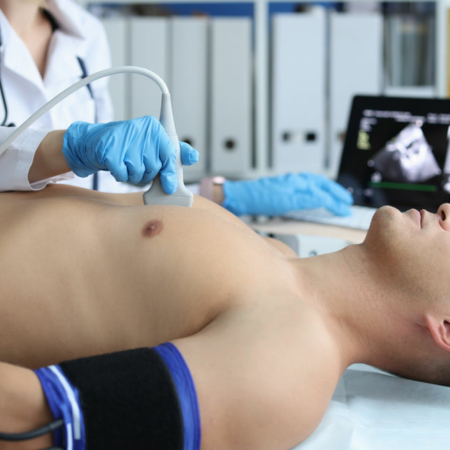
What Is a Pharmacological Stress Echocardiography?
The first subtype of stress echocardiography we’re exploring further is pharmacological echocardiology. This is where an increased heart rate is medically induced through the stimulant, Dobutamine.
During a pharmacological echocardiography, the patient will firstly be weighed to determine the amount of medication required to increase the heart rate.
The test will be performed whilst the patients’ chest is exposed whereupon a non-invasive ultrasound probe is placed. Firstly, an echo reading will be taken whilst the patient is at rest, typically on an echocardiogram bed. Following this, the same test can be undertaken after Dobutamine is administered through an IV drip, raising the heart rate artificially to the target pace.
Whilst the tests are being performed, the patient will also have their blood pressure monitored at regular intervals and have their blood oxygen levels checked.
Advantages and Limitations of Pharmacological Stress Echocardiography
Pharmacological stress echocardiography emerged as an alternative procedure for those who cannot participate in exercise.
Despite the convenience of this, and ability to offer the stress echocardiogram to a wider range of people, there are some limitations.
An artificially elevated heart rate can be uncomfortable to experience, with a longer recovery time for the heart to return to its regular pace.
There are also potential side effects and risks, however these are small and can occur in both types of stress echocardiograms. In particular, pharmacological stress tests may cause an allergic reaction to the dye (if dye is required to enhance the imaging).
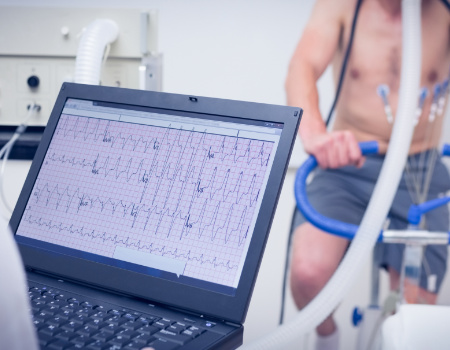
What Is a Exercise Stress Echocardiography?
The second type of stress echocardiogram is an exercise stress echocardiogram. As opposed to a pharmacological echocardiogram, an exercise echocardiogram does not artificially stimulate the heart; instead, it increases heart rate through exercise.
Exercise can be completed with a standard ergometer, but specialised equipment for echo stress cardiology will provide superior results. Once the target heart rate has been reached, the patient can stop exercising at full capacity, and begin to cool down before resting.
As with the pharmacological stress echocardiogram, an initial test will be performed at rest on a bed in order to draw comparative results. A second test can then be completed whilst the patient exercises, with the heart rate being monitored through electrode stickers on the chest. Blood pressure will also be monitored along with oxygen levels in the blood.
Whether exercising on a treadmill or an exercise bike, the patient will begin to exercise slowly, with intensity being increased until the optimal heart rate is achieved. The patient will be exerted to a sufficient level that is determined by the cardiac sonographer. Using specialised equipment allows for very accurate and smooth control of the workload.
Advantages and Limitations of Exercise Stress Echocardiography
The exercise stress echocardiogram can be a more pleasant process for patients that are able to exercise.
Whilst this process will cause shortness of breath and discomfort during exercise, it’s a more natural and pleasant testing method as opposed to artificially stimulating the heart. Heart rate will also naturally reduce once the patient stops exercising at full capacity.
This procedure can be more economical than its pharmacological counterpart in the long run, but necessitates more technical equipment to carry out. This includes either medical treadmills or custom-made exercise bed with a pedal attachment.

Which is Better, Exercise Stress or Pharmacological Stress Echocardiography?
Whilst both forms of testing have their benefits and drawbacks, it’s important that the patient’s needs determine the best stress echocardiogram procedure.
This depends on clinical information and the ability to exercise. If a patient is in poor condition, unable to walk, uncooperative or poorly motivated, or unable to reach optimum heart-rate naturally, the pharmacological stress echocardiography is recommended.
However, for those who are able to exercise, exercise stress echocardiography is the preferable method. Exercise stress echocardiography is also more suitable for heart transplant recipients.
Related Articles
Discover more expert guides
Speak to the experts
Got a question?